Case study: Derelict Fishing Gear Management System in the Adriatic Region
project information
The DeFishGear project undertook the challenge to address the need for accurate, coherent and comparable scientific data on marine litter in the Adriatic-Ionian macroregion. The DeFishGear project also piloted coordinated and harmonized actions on the science-policy-society interface for litter-free Adriatic and Ionian Seas and provided a strategic input to regional efforts in successfully achieving good environmental status in the Mediterranean Sea.description
DeFishGear project aims to facilitate efforts for integrated planning to reduce the environmental impacts of litter-generating activities and ensure the sustainable management of the marine and coastal environment of the Adriatic and Ionian Seas. Its specific objectives were:- Address the knowledge gaps and research needs to facilitate effective decision making against marine litter and its impacts;
- Address the emerging threat of microplastics;
- Pilot prevention and mitigation measures to combat marine litter in the Adriatic-Ionian macroregion;
- Enhance sub-regional cooperation in order to ensure a coordinated, coherent and integrated approach to achieve the good environmental status of the marine environment and effectively design and implement measures to address marine litter;
- Implement coordinated and harmonized actions on the science-policy-society interface for litter- free Adriatic and Ionian Seas.
- Defining a joint monitoring and assessment approach for marine litter (monitoring protocols), through a participatory process;
- Carrying out surveys on beaches, the water surface, the seafloor and biota to enhance knowledge on amounts, composition and potential impacts of marine litter;
- Establishing a Network of Experts on marine litter;
- Building capacities to monitor marine litter in a harmonized way through reinforced exchange of experiences, techniques and know-how;
- Analyzing the socio-economic implications of marine litter on people, their property and livelihoods;
- Setting up a database to make marine litter data accessible to all stakeholders;
- Developing recommendations and policy options based on the project findings and accumulated knowledge to meet regional and national objectives regarding marine litter (MSFD, RPMLMM, EcAp, etc.).
- Improved knowledge on the occurrence, amounts, sources and impacts (including socio-economic impacts) of marine litter (including microplastics) in the Adriatic;
- Harmonized marine litter monitoring activities in the Adriatic region and enhanced collaboration as a building block for future actions;
- Strengthened & reinforced science-policy interface to support the integration of sound science into policy and decision making in effectively tackling marine litter;
- Joint, coordinated and/or complementary schemes to manage human activities generating litter in the Adriatic Sea and strengthened implementation of relevant policy frameworks (Marine Strategy Framework Directive, Regional Plan for Marine Litter Management in the Mediterranean, Ecosystem Approach, Maritime Spatial Planning, Integrated Coastal Zone Management, etc.)
Policy context
The DeFishGear project provides strategic input to European and European Regional Seas efforts in successfully achieving good environmental status with regards to marine litter. The DeFishGear project is a concrete contribution to the EU Marine Strategy Framework Directive (2008/56/EC) and the related Directives (such as the Waste Framework Directive, the Packaging and Packaging Waste Directive, the Landfill Directive, Bathing Waters Directive, Urban Waste Water Treatment (UWWT) Directive, Hazardous Waste Directive, Port Reception Facilities for Ship-generated Waste and Cargo Residues Council Directive); the UNEP/MAP Regional Plan for Marine litter Management in the Mediterranean and the EU Strategy for the Adriatic and Ionian Region (EUSAIR); the International Convention for the Prevention of Pollution from Ships (MARPOL ) Furthermore, the project activities and outputs promote the implementation of the ecosystem approach and the implementation of the ICZM protocol.environmental impacts
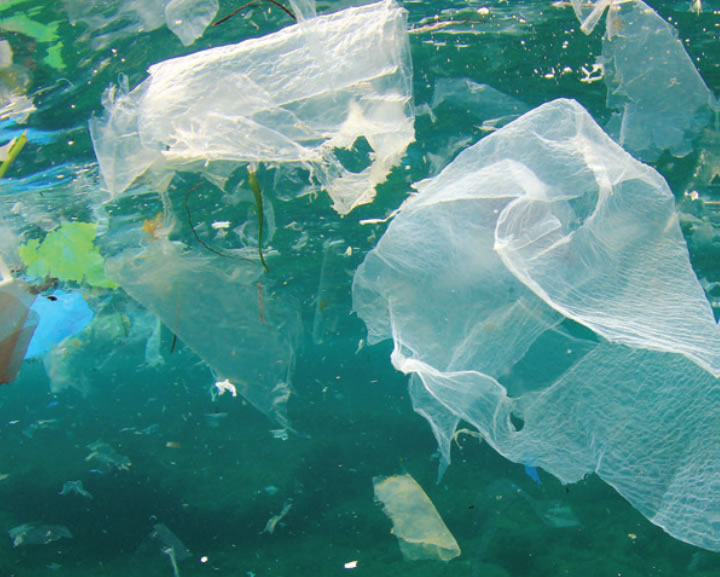
- It is known that litter in the marine environment gives rise to a range of adverse ecological impacts, including: entanglement; ingestion; smothering; disturbance and removal of habitat through beach cleaning activities; transport of invasive species; and poisoning by breakdown products.
- The project provides valuable information and strategic input to European and European Regional Seas efforts in achieving good environmental status with regards to marine litter.
- The project provided accurate, coherent and comparable scientific data on marine litter in the Adriatic and Ionian in order to set priorities for action and address marine litter effectively, thus ensuring the sustainable management and use of the marine and coastal environment of the Adriatic-Ionian macroregion.
socioeconomic impacts
The expected socio-economic impacts would be direct and indirect:- Direct, through the solutions co-developed and exploited for addressing marine litter. This is the first effort to-date aiming to assess in a coordinated, consistent, comprehensive and harmonized way the amounts, composition and to the extent possible, the sources of marine litter in all marine matrices (beaches, sea surface, seafloor, biota) of seven countries sharing the Adriatic and Ionian Seas. This is, in fact, the first of its kind marine litter assessment - at European and European Regional Seas level - which is based on comparable field data obtained for all marine compartments within the same timeframe, through the application of harmonized monitoring protocols, developed within the framework of the project, thus providing also strategic input with regards to coordinating, harmonizing and even standardizing marine litter monitoring.
- Indirect, through the increase of the participants' capacity to increased knowledge about techniques and methodologies, and improved understanding of types of marine litter, its distribution, sources and impacts, as well as suggesting management responses
- Establishment and strengthening of multi-disciplinary collaborative networks and multi-stakeholder partnerships, and fostering international cooperation in Research and Policy interface and knowledge sharing in mutually agreed terms The DeFishGear project clearly demonstrates that the increased costs and potential losses of revenue associated with marine litter for vital economic sectors such as tourism, fisheries, aquaculture and navigation are considerable, and that they negatively affect individuals, enterprises and local communities.
key lessons
The study’s results substantially add to the sketchy yet growing body of knowledge on the economic effects of marine litter. This knowledge is essential for establishing a clear and holistic understanding about the severity and scale of the harmful effects (social, economic, ecological) of marine litter in order to assist the countries of the Adriatic-Ionian macroregion in the next cycle of the EU MSFD (Member States will have to update their initial marine litter assessments by 2018) and the implementation of the Barcelona Convention Regional Plan for Marine Litter Management in the Mediterranean. Furthermore, these results feed directly into the implementation process of the EU Strategy for the Adriatic and Ionian Region that addresses a number of pressing socio-economic and environmental challenges facing the region, among which marine litter. In addition, the results can be of use to the EU Common Fisheries Policy in its role to ensure that fishing and aquaculture are environmentally, economically and socially sustainable.Project website
http://www.defishgear.netKnowledge types
Types of knowledge produced from this case study.
Geographical coverage
Beneficiaries
Beneficiaries of this case study.
-
Non-Govermental Organisation & Civil Society Organisation Croatia
-
National Public Authority of Croatia
-
National Public Authority of Croatia
-
Academic & Research Community Croatia
-
Regional or Local Public Authority of Italy
-
Academic & Research Community Italy
-
National Public Authority of Italy
-
Non-Govermental Organisation & Civil Society Organisation Italy
-
National Public Authority of Montenegro
-
Regional or Local Public Authority of Montenegro
-
Academic & Research Community Montenegro
-
Non-Govermental Organisation & Civil Society Organisation Montenegro
-
National Public Authority of Slovenia
-
Academic & Research Community Slovenia
-
Regional or Local Public Authority of Slovenia
-
Non-Govermental Organisation & Civil Society Organisation Slovenia
-
National Public Authority of Bosnia & Herzegovina
-
Academic & Research Community Albania
-
Other Economic Operator Croatia
-
Other Economic Operator Greece
-
Other Economic Operator Italy
-
Other Economic Operator Montenegro
-
Non-Govermental Organisation & Civil Society Organisation Albania
-
Regional or Local Public Authority of Albania
-
National Public Authority of Albania
-
Other Economic Operator Albania
-
Non-Govermental Organisation & Civil Society OrganisationBosnia & Herzegovina
-
National Public Authority of Bosnia & Herzegovina
-
Academic & Research Community of Bosnia & Herzegovina
-
Other Economic Operator Bosnia & Herzegovina
-
National Public Authority of Greece
-
Regional or Local Public Authority of Greece
-
Academic & Research Community Greece
-
Non-Govermental Organisation & Civil Society Organisation Greece
-
Other Economic Operator Slovenia
Related Policies
Which EU policy requirements and EU Directives were aimed at being addressed by the project or which national and/or regional policy challenges and/or requirements aimed to be addressed?
-
EU Marine Strategy Framework Directive (2008/56/EC)
-
EU Waste Framework Directive
-
EU Packaging and Packaging Waste Directive
-
EU Landfill Directive
-
EU Bathing Waters Directive
-
EU Urban Waste Water Treatment (UWWT) Directive
-
EU Hazardous Waste Directive
-
UNEP/MAP Regional Plan for Marine litter Management in the Mediterranean
-
EU Strategy for the Adriatic and Ionian Region (EUSAIR)
-
International Convention for the Prevention of Pollution from Ships
-
EU Water Framework Directive
-
EU Port Reception Facilities for Ship-generated Waste and Cargo Residues Council Directive
-
Barcelona Convention UNEP/MAP
Funding mechanism
Availability/accessibility of knowledge outputs online
Legal entity types
Types of consortium members involved in this case study.